Nanoparticles for siRNA delivery
RNAi gene silencing technologies have shown significant potential for treating various diseases, including cancer. However, clinical success in cancer therapy remains elusive, mainly owing to suboptimal in vivo delivery of RNAi therapeutics. We developed a library of ultra-pH-responsive polymers and demonstrated the utility of these materials in targeted and deep tumor-penetrating nanoparticle (NP) for in vivo RNAi. The new NP platform is mainly composed of the following key components: i) internalizing RGD (iRGD) to enhance tumor targeting and tissue penetration; ii) polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains to prolong blood circulation; and iii) sharp pH-responsive hydrophobic polymer to improve endosome escape.
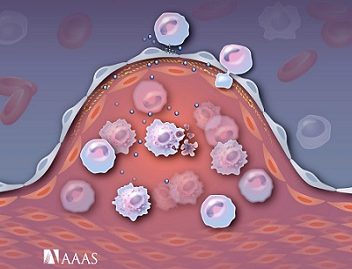
Inflammation Resolving Nanoparticles.
Excessive inflammation and failed resolution of the inflammatory responses are underlying components of numerous conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Unfortunately, controlled delivery of the inflammation-resolving therapeutics to lesions is challenging. Thus, we design novel nanoformulations capable of carrying the inflammation-resolving therapeutic drugs to the inflammatory lesions efficiently, and demonstrate their therapeutic efficacy and pro-resolving potential in diverse animal models. This technology provides a step closer to the development of novel therapeutic nanoplatforms for inflammatory disease treatment.
Publications:
- Kamaly N, Fredman G, Fojas JJ, Subramanian M, Choi WI, Zepeda K, Vilos C, Yu M, Gadde S, Wu J, Milton J, Carvalho Leitao R, Rosa Fernandes L, Hasan M, Gao H, Nguyen V, Harris J, Tabas I, Farokhzad OC. Targeted Interleukin-10 Nanotherapeutics Developed with a Microfluidic Chip Enhance Resolution of Inflammation in Advanced Atherosclerosis. ACS Nano. (2016 ) Apr 28. Full Text
- Gabrielle Fredman, Nazila Kamaly, Stefano Spolitu, Jaclyn Milton, Devram Ghorpade, Raymond Chiasson, George Kuriakose, Mauro Perretti, Omid Farokzhad and Ira Tabas, Targeted nanoparticles containing the proresolving peptide Ac2-26 protect against advanced atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Science Translational Medicine, 7(2015) 275ra20. Full Text
- Kamaly N, Fredman G, Subramanian M, Gadde S, Pesic A, Fayad ZA, Langer R, Tabas I, Farokhzad OC. Development and in vivo efficacy of targeted polymeric inflammation-resolving nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 10(2013) 6506. Full Text
Oral Delivery
Oral administration is considered the most favorable route of administration than injection because of convenience and compliance by patients, resulting in improved treatment efficacy, but it is challenging for biologic drugs like insulin. In our lab, we designed a novel multi-stage nanoparticle delivery system designed to overcome all of the barriers of the gastrointestinal tract and provide efficient oral delivery of insulin. In which the nanoparticles will protect the biologic from the adverse environment in the gastrointestinal tract, get actively transported across the intestinal barrier, and rapidly release their payload to effectively deliver and maximize the efficacy of the biologic. This technology is expected to have a significant impact on diseases that are currently limited to injection-based therapies, notably diabetes.
References
- Pridgen EM, Alexis F, Kuo TT, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Karnik R, Blumberg RS, Langer R, and Farokhzad OC, “Transepithelial transport of fc-targeted nanoparticles by the neonatal fc receptor for oral delivery” Science Translational Medicine, 5, 213ra167 (2013). PMCID: PMC4023672. Full Text
- Wu J, Kamaly N, Shi J, Zhao L, Xiao Z, Hollett G, John R, Ray S, Xu X, Zhang X, Kantoff PW and Farokhzad OC, “Development of multinuclear polymeric nanoparticles as robust protein nanocarriers” Angewandte Chemie International Edition 53 (34), 8975-8979 (2014). PMCID:PMC4143165. Full Text
- Lim JM, Swami A, Gilson LM, Chopra S, Choi S, Wu J, Langer RS, Karnik R, and Farokhzad OC, “High-throughput synthesis of nanoparticles in a versatile coaxial turbulent jet mixer” ACS Nano 8, 6056-6065 (2014). PMCID:PMC407240. Full Text
- Choi W, Kamaly N, Riol-Blanco L, Lee IH, Wu J, Swami A, Vilos C, Yameen B, Yu M, Shi JJ, Tabas I, von Andrian UH, Jon S, and Farokhzad OC, “A solvent-free thermosponge nanoparticle platform for efficient delivery of labile proteins” Nano Letters 14 (11), 6449-6455 (2014). PMCID: PMC4245989. Full Text
- Zhu X, Xu Y, Solis LM, Tao W, Wang L, Behrens C, Xu X, Zhao L, Liu D, Wu J, Zhang N, Wistuba II, Farokhzad OC, Zetter BR, Shi J., Long-circulating siRNA nanoparticles for validating Prohibitin1-targeted non-small cell lung cancer treatment, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2015) Jun 23;112(25):7779-84. Full Text
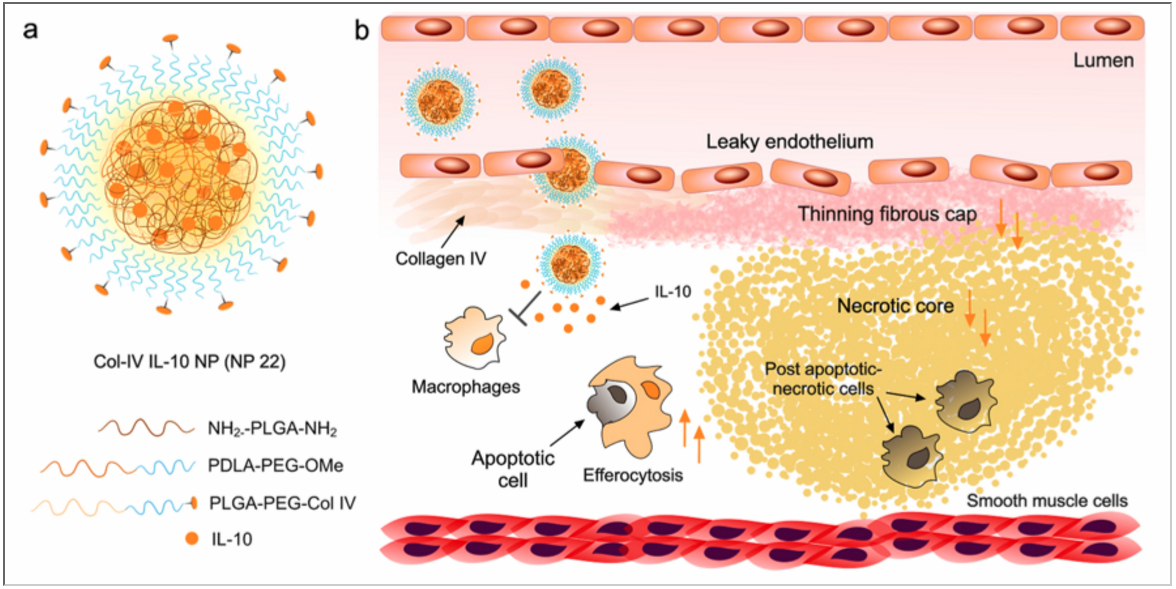
Targeted anti-atherosclerosis polymeric nanoparticles delivering inflammation-resolving proteins
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arteries and the leading cause of death worldwide. Therapeutics that can temper inflammation using the body’s innate mechanisms are powerful complementary strategies to existing treatments. Our research team in collaboration with Prof. Ira Tabas from Columbia University have developed a polymeric nanoparticle using a rapid microfluidic platform enabling the production of small and robust nanoparticles effectively entrapping IL10 protein (an anti-inflammatory cytokine), in a matter of minutes. The nanoparticles also have a targeting ligand for plaque retention and therefore the ability to release IL-10 in a spatiotemporal manner. These findings were recently published in ACS Nano.
Read More: